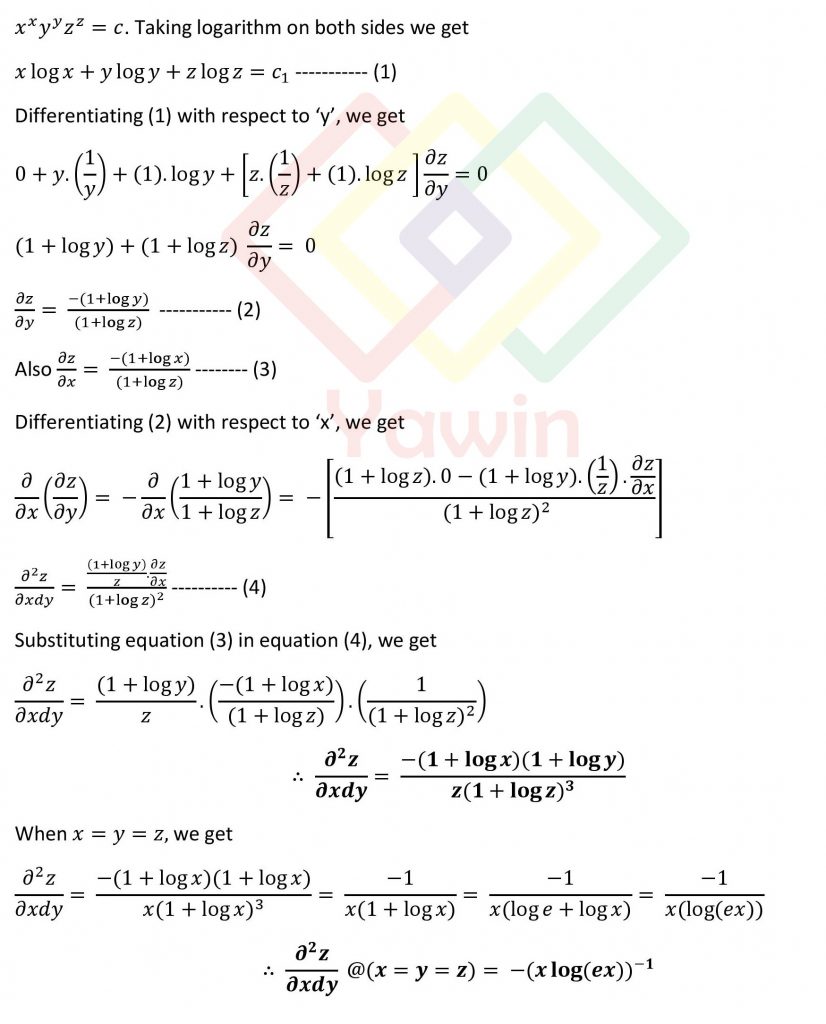
if x^x y^y z^z=c show thatn (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(1+logx)(1+logy)/(z(1+logz)^3) and hence deduce that (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(xlog(ex))^-1 when x=y=z
Question

Solution
Question
if x^x y^y z^z=c show thatn (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(1+logx)(1+logy)/(z(1+logz)^3) and hence deduce that (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(xlog(ex))^-1 when x=y=z
Type 1 Questions
- if u=x^3-3xy^2+x+(e^x cosy)+1, show that ((∂^2 u)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂y^2))=0
- if u= log((x^2+y^2)/(x+y)), show that xu_x+yu_y=1
- if u=tan^(-1)(y/x), verify that (∂^2 u)/(∂y ∂x) = (∂^2 u)/(∂x ∂y)
- if u=e^(ax+by)f(ax-by), prove that (b ∂u/∂x)+(a ∂u/∂y)=2abu
- if u=1/√(x^2+y^2+z^2), then show that ((∂^2 u)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂y^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂z^2))=0
- if u=log√(x^2+y^2+z^2), then show that (x^2+y^2+z^2)(((∂^2 u)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂y^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂z^2)))=1
Type 2 Questions
- if x^x y^y z^z=c show thatn (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(1+logx)(1+logy)/(z(1+logz)^3) and hence deduce that (∂^2 z)/∂x∂y=-(xlog(ex))^-1 when x=y=z
- if x=rcosθ and y=rsinθ, prove that ((∂^2 r)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 r)/∂y^2))=1/r [(∂r/∂x)^2+(∂r/∂y)^2] and ∂r/∂x=∂x/∂r
- if r^2=(x-a)^2+(y-b)^2+(z-c)^2, show that ((∂^2 r)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 r)/∂y^2))+((∂^2 r)/∂z^2))=2/r
- if u=f(r), where r=√(x^2+y^2+z^2), then show that ((∂^2 u)/(∂x^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂y^2))+((∂^2 u)/(∂z^2))=f”(r)+(2/r)f'(r)
Related Topics
- Trigonometry Formula
- Differentiation Formula List
- Taylor’s Theorem, Taylor’s Series
- Maclaurin’s Theorem, Maclaurin’s Series
- Indeterminate Forms
- Partial Derivatives
